STUDY CASE / SIMULATION
GRIEVANCE REDRESS MECHANISM (GRM)

Agenda
Spectrum Grievance
Benchmarking GRM
GRM Procedure and Workflow

1
2
3

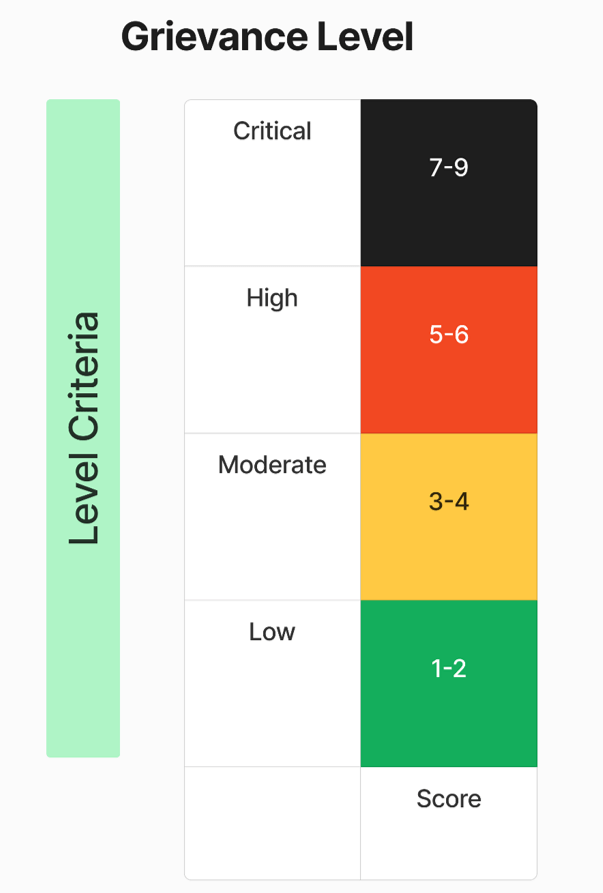
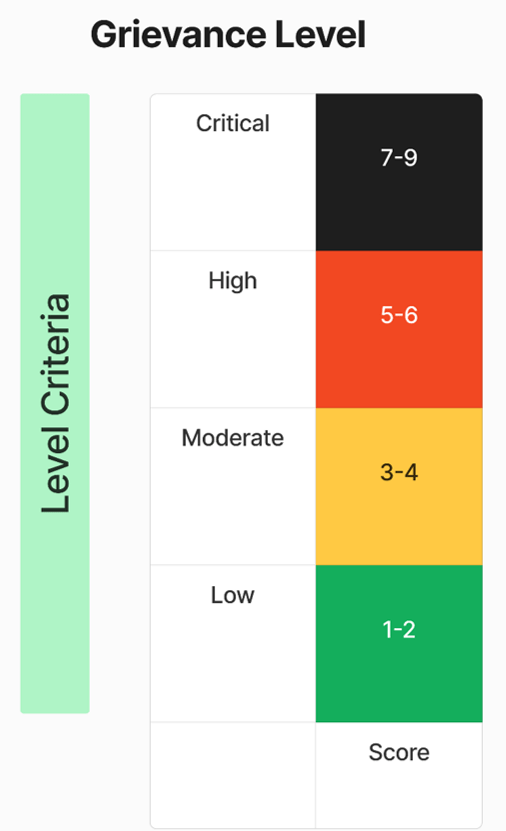
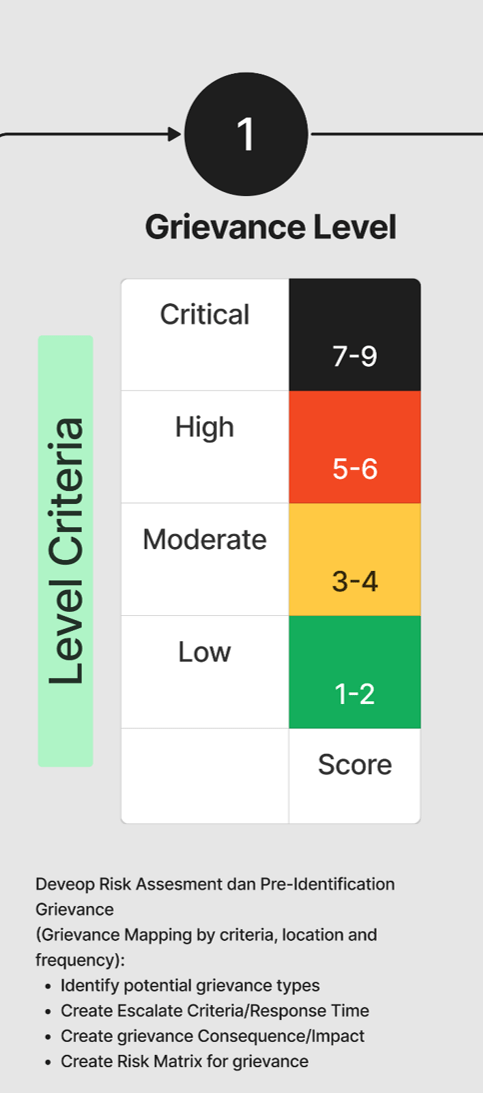
Assessment Level of Grievance

Develop Assessment/Mapping of Grievance
1

Impact Criteria Grievance:

Environmental Risk
Community Relation (Social)
Economic Risk

1
2
3
Regulatory Risk
4

Impact criteria grievance
Criteria: 1. Environmental Risk
Description:
Includes water pollution, air pollution, soil contamination, biodiversity loss, and noise pollution. Harm to nature, like water pollution, air emissions, or land damage from mining. Examples: Chemical spills, dust from smelters, deforestation. Can hurt communities, wildlife, or Vale’s reputation, triggering complaints and costs.
Scoring/ Scale (1-3):
1: No or very little impact on the environment.
2: Limited pollution occurs (e.g., medium concentration of wastewater, small-scale chemical leakage), leading to localized effects but manageable in the short term.
3: Large-scale environmental damage, such as oil spills, deforestation, or water pollution leading to the extinction of local species.

Criteria: 2. Community Relations (Social)
Description:
Social conflicts, including land disputes, inadequate consultation, cultural heritage impacts, and lack of trust or social license. Covers land disputes, inadequate consultation, cultural heritage impacts, and trust issues. Examples: Conflicts over mining on traditional land, lack of jobs for locals. Can lead to protests or distrust, disrupting operations.
Scoring/ Scale (1-3):
1: The impact is minor, affecting only a small number of people or causing minimal disruption to the company's operations, and can be easily managed.
2: The impact is moderate, affecting a larger portion of the community or causing temporary operational disruptions that require more effort to address.
3: The impact is significant, causing major disruption to company operations or affecting many people, and may require substantial efforts to rebuild relationships or address the issue

Impact criteria grievance
Criteria: 3. Economic Risk
Description:
Economic effects on local communities, like impacts on livelihoods (e.g., fishing, farming), economic dependence, dependence on mining, and supply chain disruptions. Financial impacts on locals, like reduced livelihoods from mining. Examples: Lower fishing yields due to water use, fewer crops from land changes. Can spark complaints and demand compensation, raising costs.
Scoring/ Scale (1-3):
1: The impact is minor, affecting only a small number of people or causing minimal disruption to the company's operations, and can be easily managed.
2: The impact is moderate, affecting a larger portion of the community or causing temporary operational disruptions that require more effort to address.
3: The impact is significant, causing major disruption to company operations or affecting many people, and may require substantial efforts to rebuild relationships or address the issue

Impact criteria grievance
Criteria: 4. Regulatory Risk
Description:
Involves permit violations, non-compliance, and legal challenges. Breaking rules or laws, like mining permits or environmental standards. Examples: Missing permits, exceeding emission limits, non-compliance with UU Minerba. Can lead to fines, shutdowns, or legal battles, hitting Vale hard.

Scoring/ Scale (1-3):
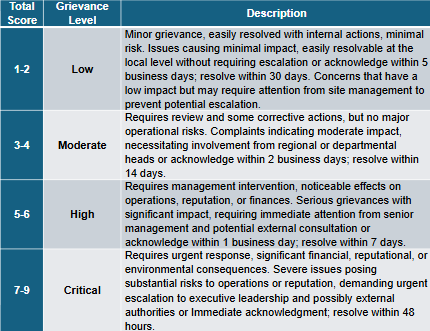
1: The impact is minor, causing minimal disruption to operations or affecting only a small part of operations that can be resolved quickly. Example: A small fine or warning that can be resolved immediately without causing major disruptions in company operations.
2: The impact is moderate, causing disruptions or fines that affect operations and may require some time for resolution, but does not lead to shutdowns or significant reputational damage. Example: Non-compliance with environmental policies that results in moderate fines or temporary suspension of some operational activities, but the company can recover with proper effort.
3: The impact is significant, causing major disruptions that can affect the company’s reputation, lead to operational shutdowns, or trigger costly legal challenges. Example: Failing to comply with the Minerba Law or exceeding emission limits, resulting in large fines, mine closures, or legal actions that may affect the company’s ongoing operations.

Scoring Method
Risk Score: Multiply likelihood by impact (1-9).
Likelihood: Rate as Low (1, unlikely), Medium (2, possible), High (3, likely).
Impact: Rate as Low (1, minor), Medium (2, moderate), High (3, severe).
Grievance Levels: Low (1-2), Moderate (3-4), High (5-6), Critical (7-9)

Example:
Water pollution might score high (9) if likely (3) and severe (3) due to health impacts.
= 3 x 3 = 9 (score)

Reference:
Kemp, D., & Bond, C. J. (2015). “Mining and Community Grievances: A Case Study Analysis.” Resources Policy, 45, 256-263.
-
Supports clear roles (e.g., GA for coordination, GC for oversight) scaling with grievance severity (Low to Critical) in mining GRMs.
-
Access: ScienceDirect.
World Bank (2014). “Grievance Redress Mechanisms: A Global Review.”
-
Highlights defined roles (e.g., administrators, committees, specialists) to match grievance urgency, cutting costs by 30%, as noted in Roles doc (p. 4).
-
Access: World Bank.
Rees, C., & Vermijs, D. (2011). “Mapping Grievance Mechanisms in the Business and Human Rights Arena.” Harvard Kennedy School, Corporate Social Responsibility Initiative.
-
Details roles like GA for daily tasks and GC for strategic decisions, tied to severity-based prioritization in GRMs.
-
Access: Harvard.
International Council on Mining and Metals (ICMM) (2019). “Handling and Resolving Local-level Concerns and Grievances.”
-
Recommends role clarity (e.g., departments for expertise, GC for approvals) to handle grievances by impact, aligning with Vale’s structure (Roles doc p. 1-3).
-
Access: ICMM.
Vale Sustainability Report (2023).
-
Confirms stakeholder engagement teams (e.g., Community Relations) and governance boards (e.g., GC), supporting roles in GRM operations.
-
Access: Vale.

SIMULATION

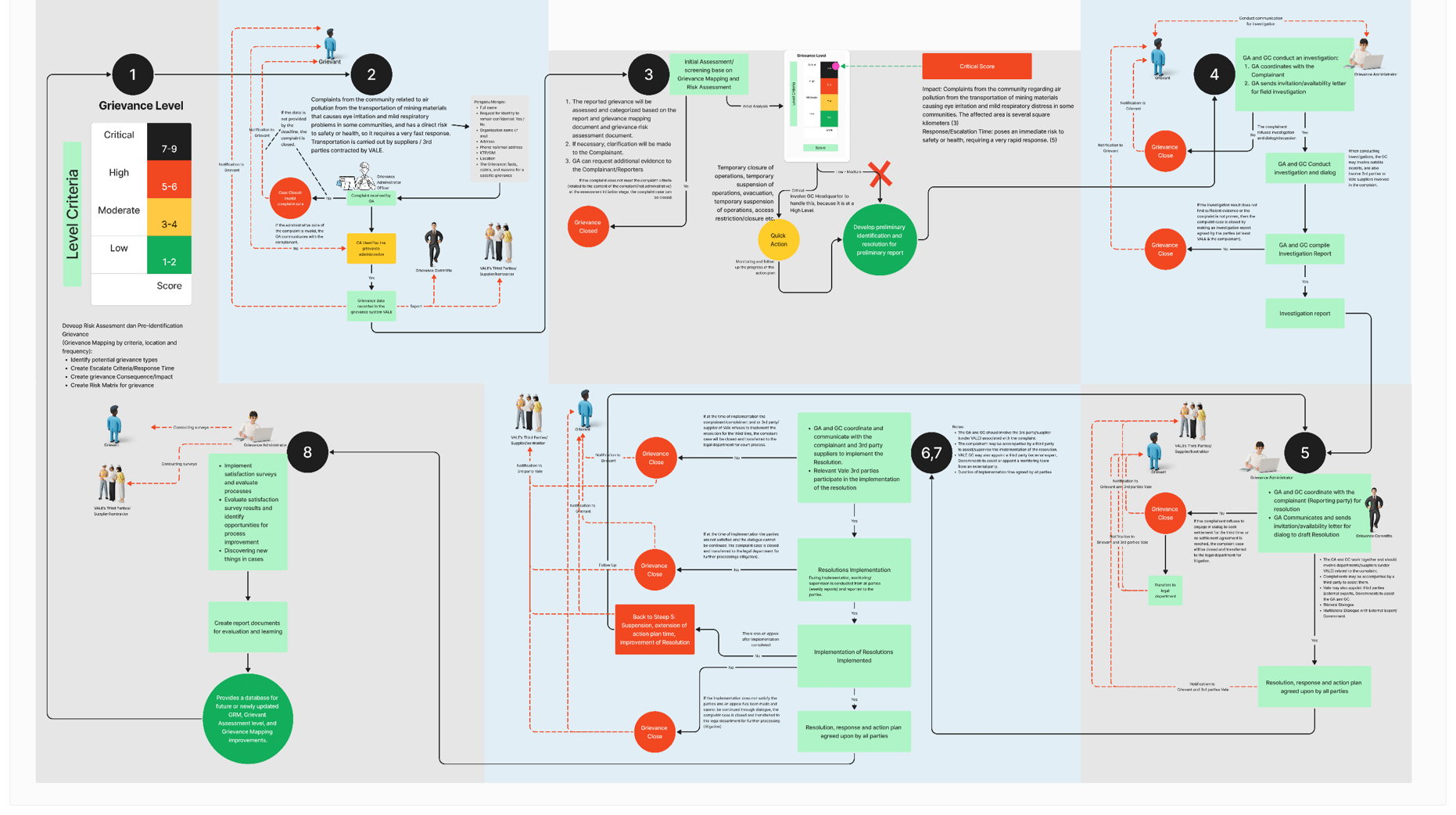

Grievance Assessment and Mapping can be built from social mapping data, Environmental Impact Assessment data and previous grievance report data.
Developing Grievance Mapping-Grievance Assessment Level
1

Receipt and Recording
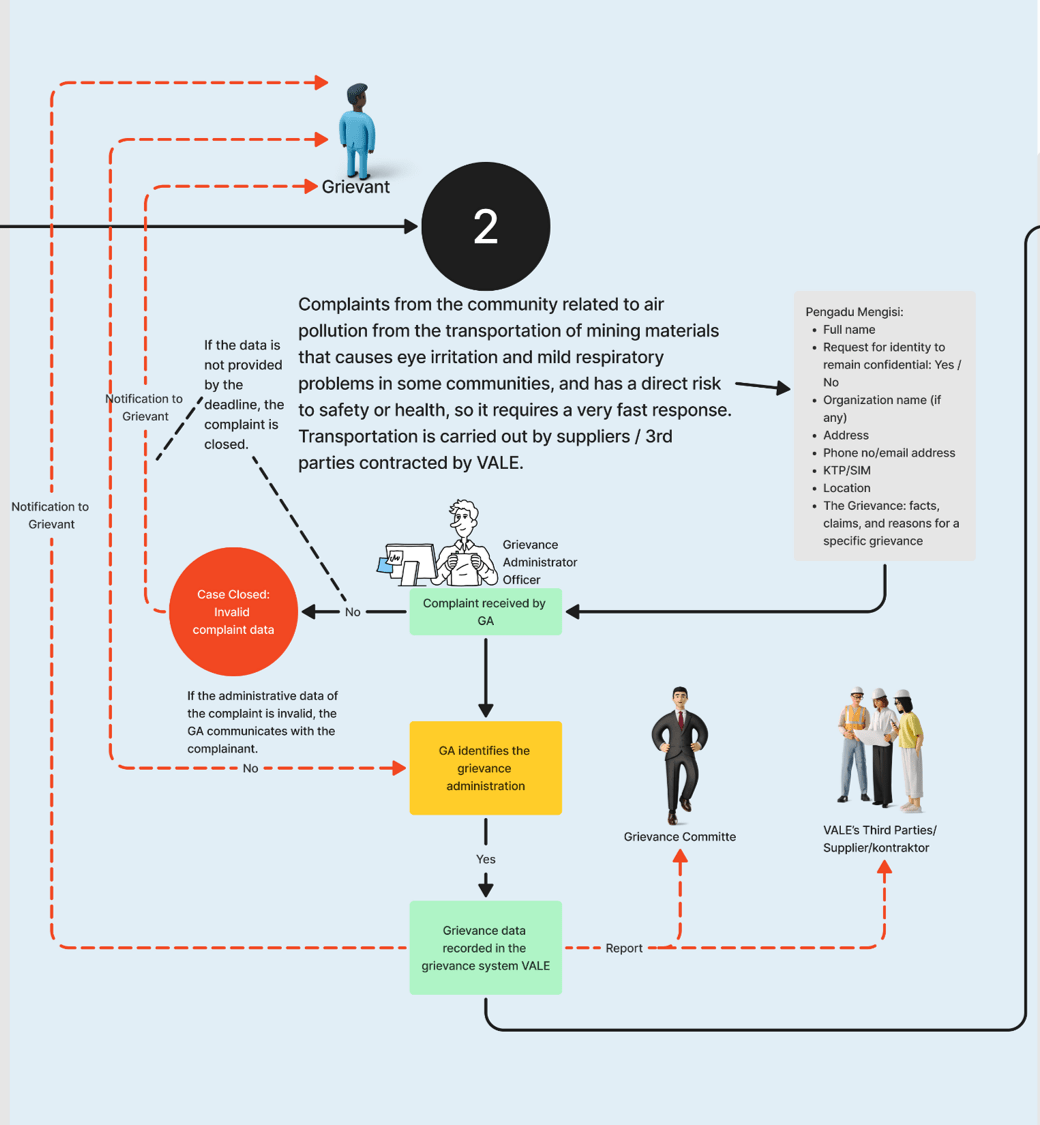
2

Assessment and Categorization
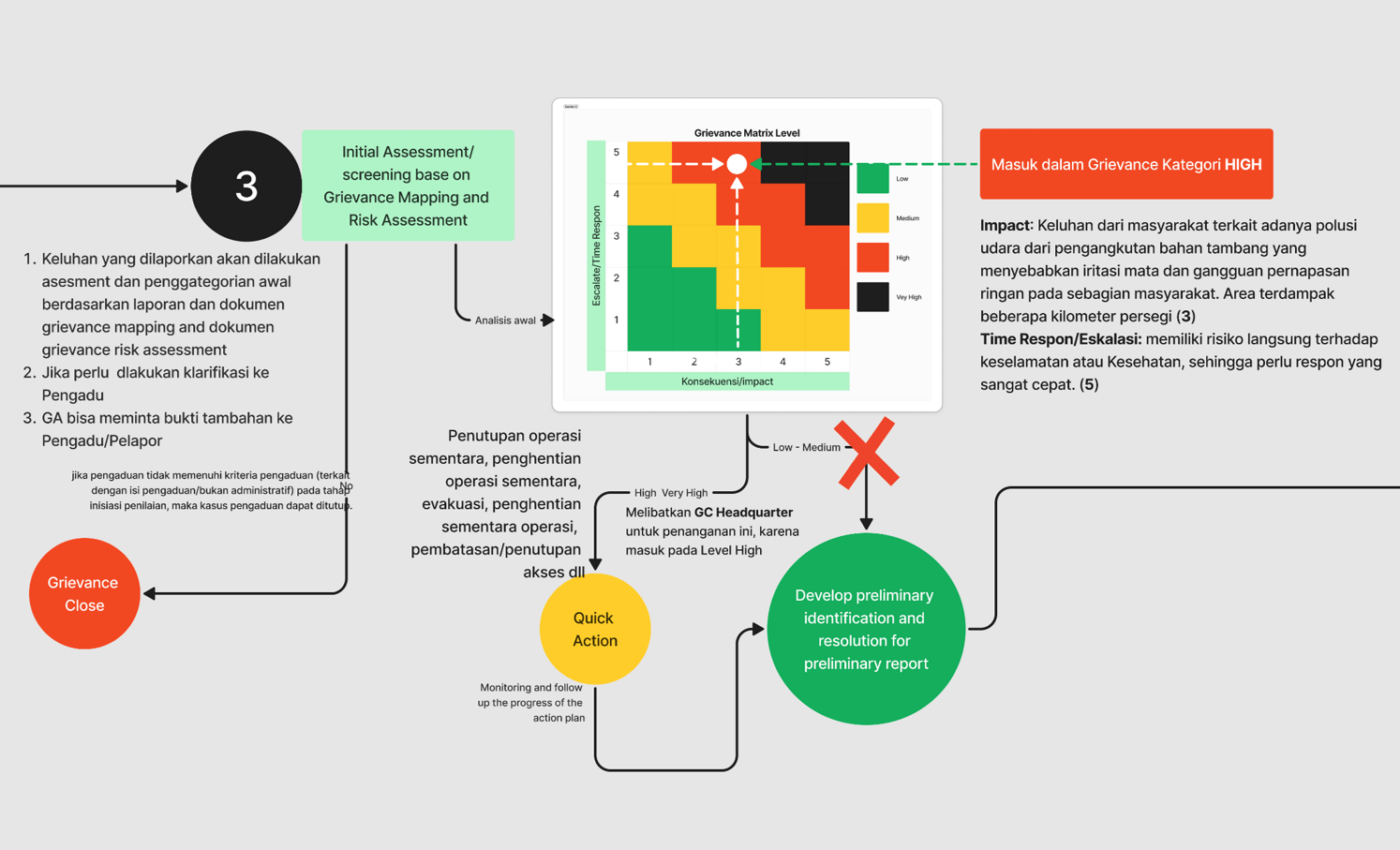
3

Reporting and Investigation
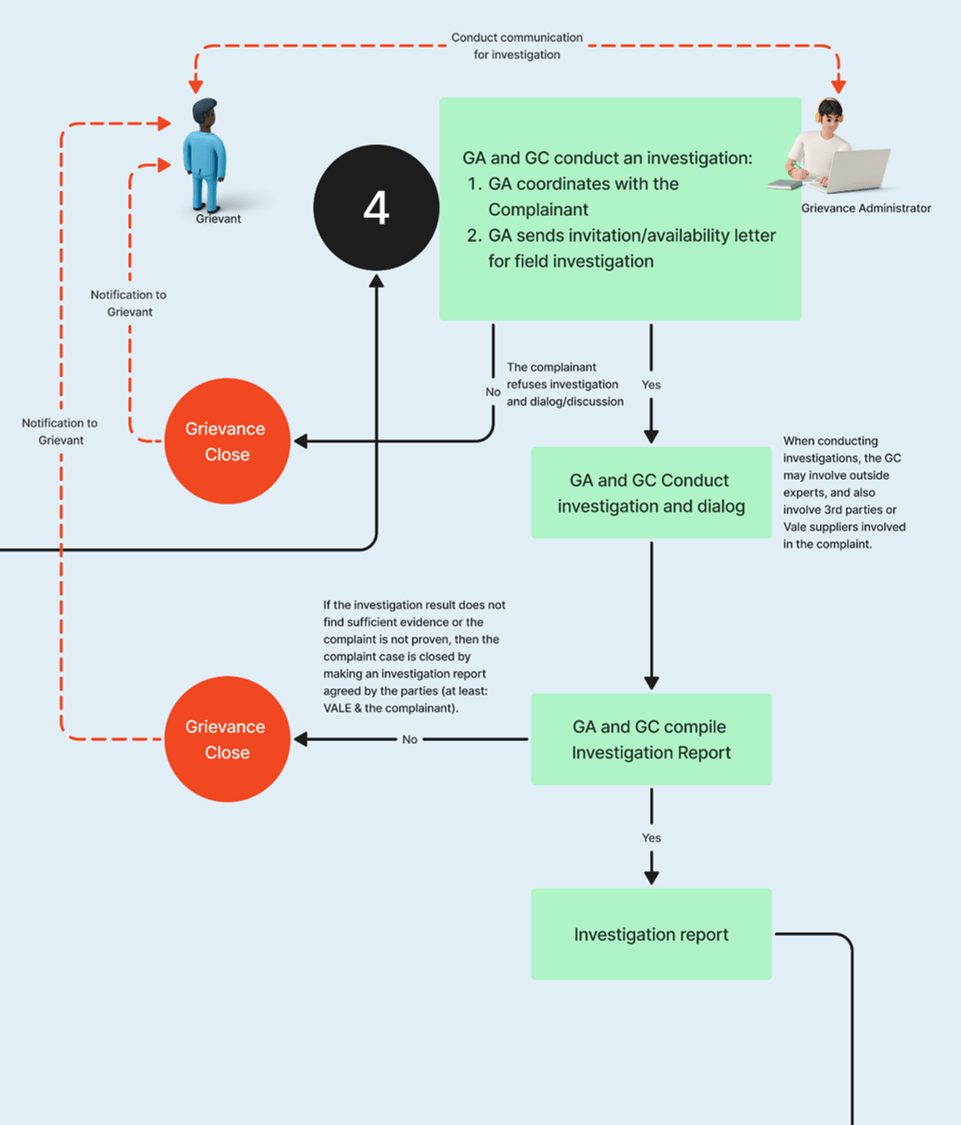
4

Develop Resolution, response and action plan
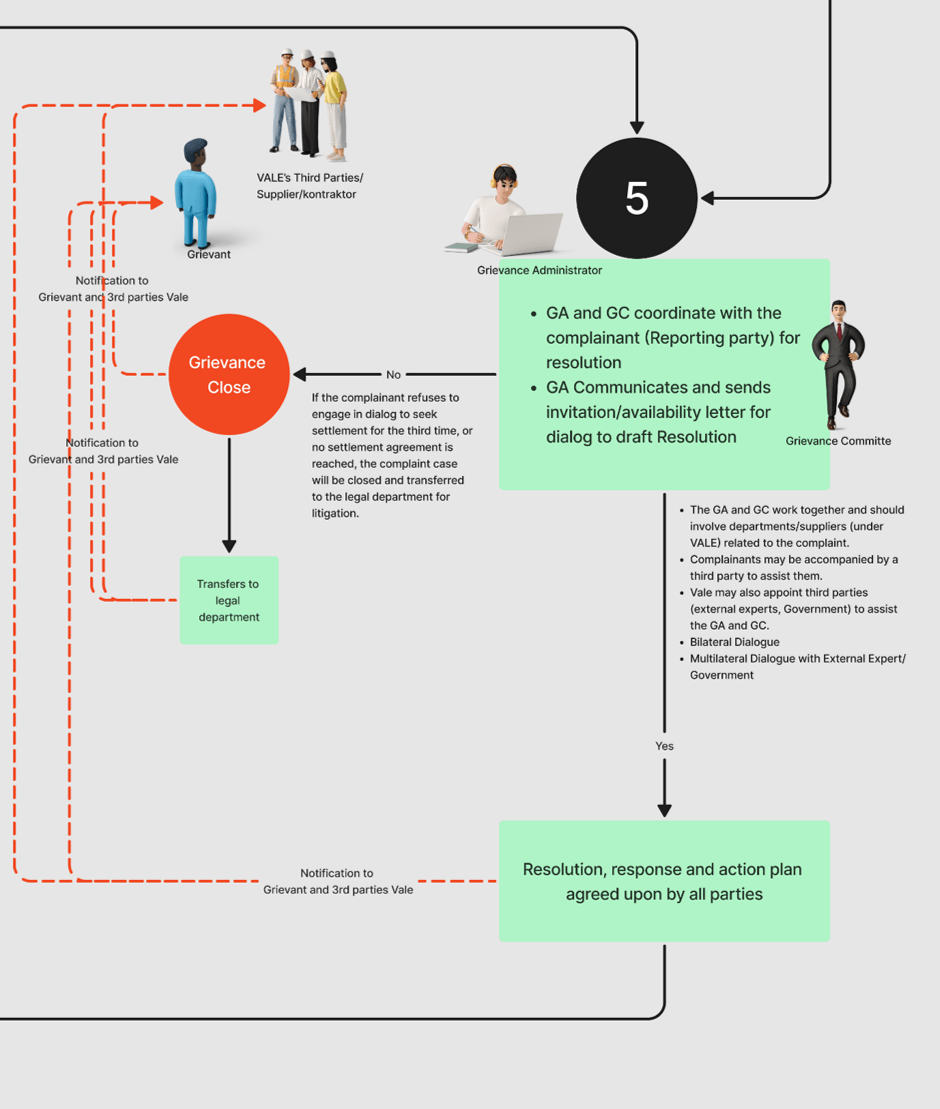
5

Resolution/action plan implementation and communication & Monitoring and Follow up
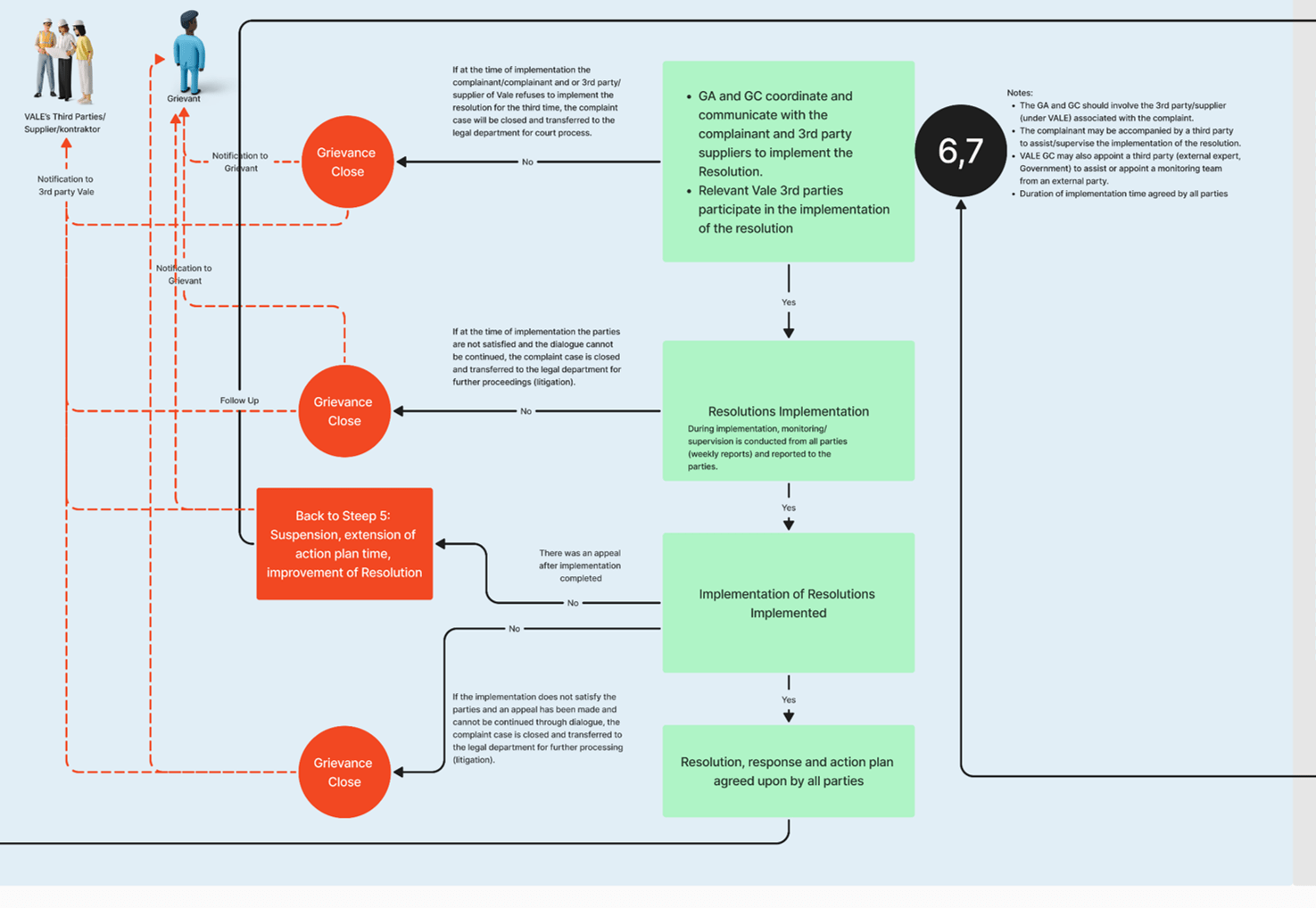
6-7

Evaluating and Learning
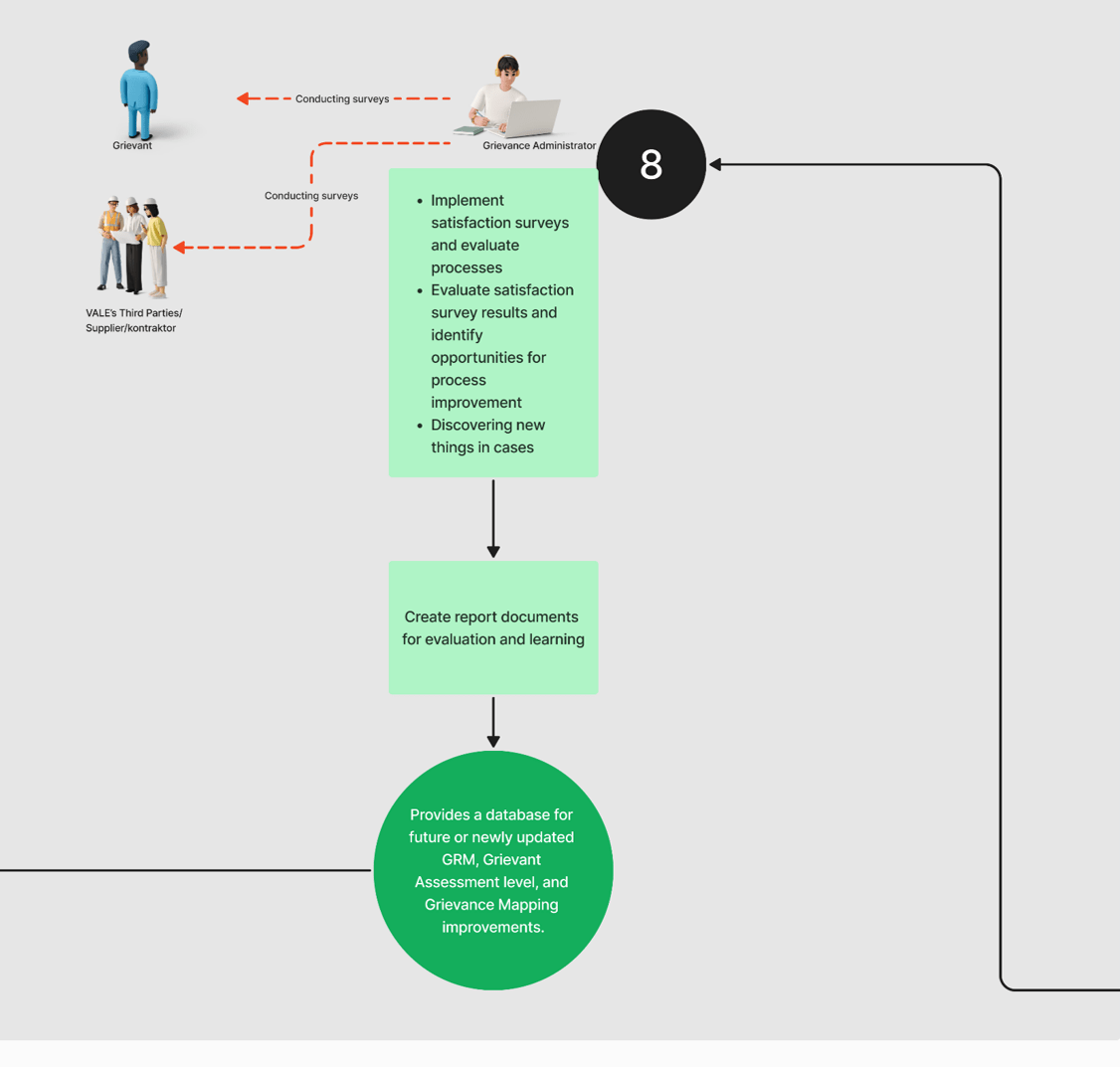
8

Discussion


Thank You
